Arm Moves to Factor AI into Chip Design with New CPU, GPU

Arm's disciplined philosophy of power efficiency first helped the company thrive in smartphones, and leave Intel and its PC-based mobile chips in the dust.
The chip designer is not abandoning its principles in the new era of AI computing, with a new chip architecture that provides a glimpse at how it will design its future chips.
Arm introduced a new Cortex-X4 high-performance core and a GPU called G720 this week, which are targeted at mobile devices.
The chipset, which also includes the Cortex-A720 performance cores and Cortex-A520 power-efficiency CPUs, can be paired with GPUs in smartphones, tablets, and PCs.
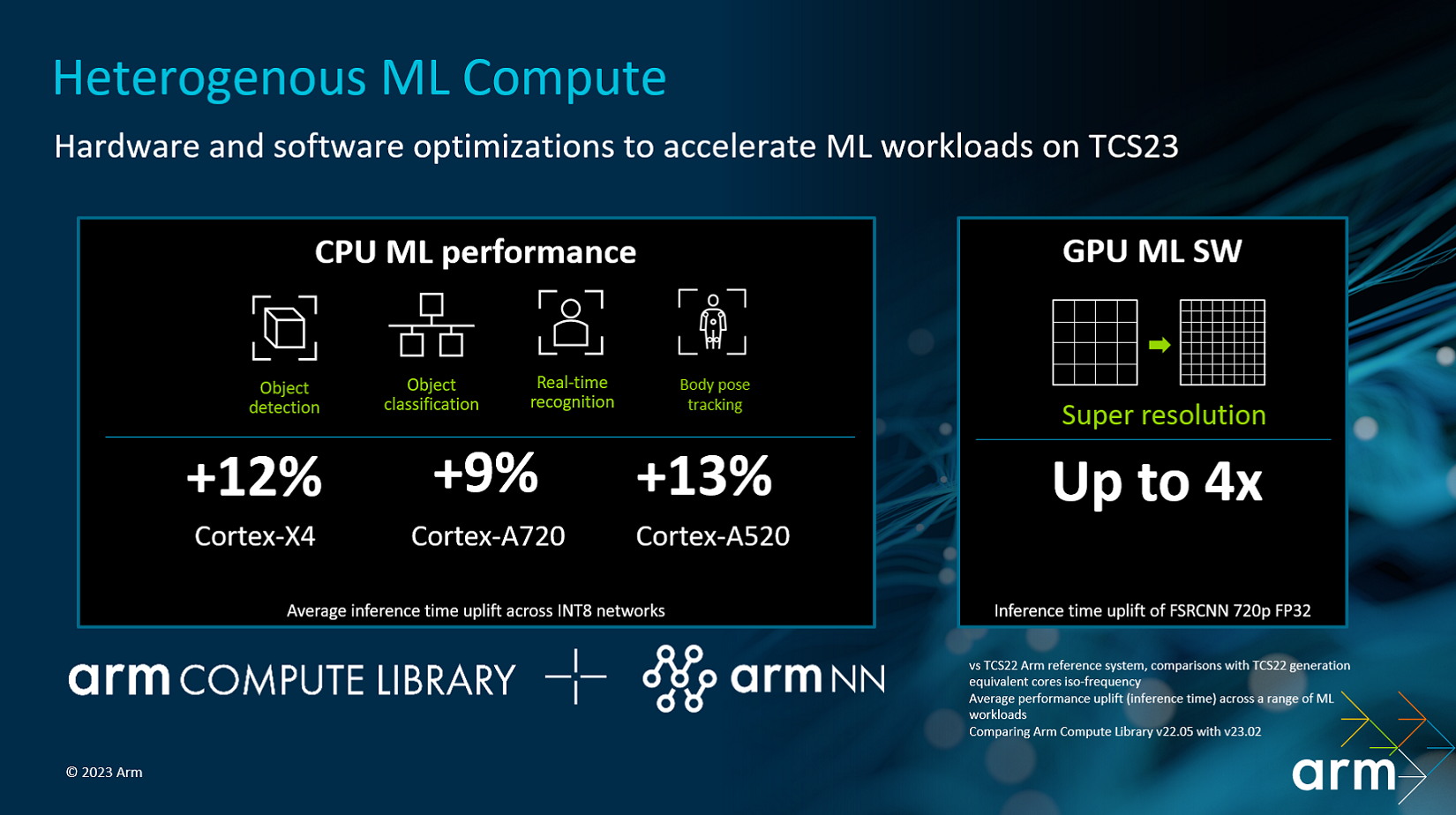
The chipset package, called TCS23, has a mix of hardware and software technologies operating on the sidelines that improve AI performance.
The new CPUs and GPU pack in more performance and power efficiency than its predecessor Cortex-A3, which was released last year.
The Cortex-X4 delivers 15 percent more performance and consumes 40 percent less power than Cortex-X3, Arm said.
Arm measured 12 percent faster machine-learning performance in Cortex-X4 compared to last year’s Cortex-A3. The company measured 9 percent better ML performance for Cortex-A720 (compared to previous-generation Cortex-A710), and a 13 percent improvement for Cortex-A520 compared to last year’s Cortex-A510.
Arm noted a significant speed boost – up to 4x – in upscaling images on its G720 GPU with code optimized for the Fast Super-Resolution Convolutional Neural Network.
The GPU also uses machine-learning features to restructure 3D scenes. The G720 GPU achieves 25 percent more peak performance and 22 percent less memory bandwidth usage than its predecessor G715, the company said in a blog entry.
A chipset includes 8 CPUs (one Cortex-X4 CPU, five Cortex-A720 CPUs, and two Cortex-A520 CPUs), which boosts the number of high-performance cores while cutting down the low-power A520 cores. But even the low-power CPU is empowered with the elimination of 32-bit mode and support for only 64-bit applications.
“Being 64-bit only helps our partners deliver greater computing performance and more security and ML features, while improving the app development process," Arm said in a separate blog entry.
The 64-bit-only support loads applications up to 20 percent faster, and "this helps to meet the insatiable demand for more computing across various workloads, particularly for AI and AAA gaming," Arm said.
The reasoning for chip makers to cut off 32-bit support is that most applications and operating systems, like Windows 11, are available only in 64-bit mode.
Intel is also looking to move exclusively to a 64-bit chip architecture with a new x86S ISA.
The new Arm chip designs also trained algorithms from Unity Technologies to balance power consumption between CPUs and GPUs.
The chip supports about 100 of Unity's ML agents that use AI to predict the behavior of characters or simulations. The pre-processing reduces the load of GPUs and CPUs to draw up scenes from scratch. This is a new feature on Arm’s mobile chipsets.
Google, Qualcomm, Apple, Samsung, and others have developed their own neural processors, which they put on chips based on Arm architecture. Arm provides chip blueprints and the customized neural chips are put on top of the Arm CPU. Many chip companies have licensed Arm's GPU designs.
Arm said it "remains committed to developing and testing our GPUs against new applications for machine learning."