Updated: AT&T, Dell Partner to Advance 5G Cloud

AT&T added to its growing list of 5G wireless partnerships this week, announcing collaboration with Dell Technologies to develop “cloud-oriented 5G” wireless infrastructure built upon an open source tools used to automate cloud provisioning.
Among the goals of this and other partnerships is leveraging 5G's higher data rates along with infrastructure upgrades to handle high-end workloads at the network edge.
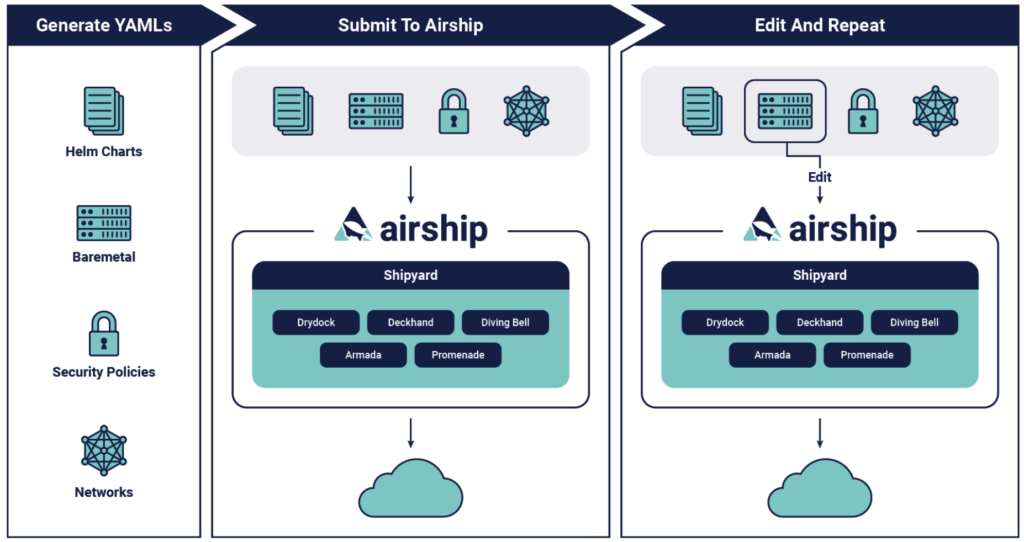
The centerpiece of the AT&T-Dell alliance is Airship, a container-based open infrastructure initiative. Along with cloud provisioning, Airship also manages datacenter infrastructure to deliver what founders describe as “production-grade” Kubernetes clusters.
The other key component of delivery mechanism is a workflow language called YAWL. So-called “declarative” YAWL files are used to describe an Airship environment, thereby allowing operators to manage infrastructure deployments.
AT&T and Dell announced this week they will align their 5G cloud strategy around Airship and AT&T’s Network Cloud to disaggregate 5G networks and promote open infrastructure. Along with automated cloud provisioning, application containers orchestrated by a Kubernetes cluster API would handle infrastructure monitoring.
Among the goals of 5G wireless deployments is boosting edge computing capabilities for the Internet of Things. The partners are betting the combination of 5G and edge computing would extend the reach of cloud deployments to the network fringes where innumerable connected devices will be installed.
The 5G partnership is among the latest edge computing initiatives that seeks to leverage networking advances and 5G bandwidth to help move computing closer to edge applications. Infrastructure vendors are forging distributed architectures using software-defined networks that move away from proprietary plumbing to embrace open frameworks. That architecture is seen as the best way to reduce network latency, laying the foundation for a new class of 5G-driven, cloud-native applications.
“To capitalize on the new business opportunities that edge computing and 5G will create, communication service providers need open, validated, industry-standard architectures, combined with software-defined networking, network functions virtualization, cloud-native applications and multi-access edge computing,” the partners said in announcing the 5G collaboration on Thursday (Aug. 15).
While AT&T (NYSE:T) will seek to open up its network cloud via Airship, Dell said it would deliver open source automation capabilities ranging from bare metal to its networking and storage infrastructure.
“This collaboration will not only enable us to accelerate the AT&T Network Cloud on the Dell Technologies infrastructure, but also further the broader community goal of making it as simple as possible for operators to deploy and manage open infrastructure in support of [software-defined networks] and other workloads,” said Amy Wheelus, vice president of AT&T Network Cloud.
Along with integrating the Kubernetes cluster API to orchestrate software container delivery, the partners also said they would promote Airship and other open source projects, including OpenStack Ironic bare metal provisioning and Metal3, the bare metal host provisioning tool for Kubernetes.
With Dell (NYSE: DELL) onboard, AT&T also said it would promote the 2.0 release of Airship that would accelerate automated deployment and management of Kubernetes along with cloud software running across bare metal and cloud infrastructure.
The current version of Airship, available here, is designed to manage datacenter plumbing—starting with “raw” bare metal infrastructure. That infrastructure is managed via descriptive YAWL (“yet another workflow language”) files, eliminating the need for orchestration tooling to automate the container delivery mechanism.
Application containers and OpenStack Helm, which is used to deploy OpenStack on Kubernetes, also are used to push orchestration capabilities to the network edge. Proponents assert that expanding the software stack requires little more than adding new Helm “charts” to Airship declarations.
The result, they add, is a self-hosted platform in which Airship components deployed by Helm run as Kubernetes services. They can then be upgraded as with software components.
AT&T's partnership with Dell, IBM (NYSE: IBM) and others looks to put that open infrastructure for automated cloud provisioning to the test as high-performance 5G applications are rolled out at the network edge.
Related
George Leopold has written about science and technology for more than 30 years, focusing on electronics and aerospace technology. He previously served as executive editor of Electronic Engineering Times. Leopold is the author of "Calculated Risk: The Supersonic Life and Times of Gus Grissom" (Purdue University Press, 2016).