Revolutionizing the Storage Pyramid with Intel® Optane™ Technology Sponsored Content by Intel
Despite improvements along the way, the storage pyramid hasn’t experienced dramatic innovation since solid state drives based on 3D NAND technology went mainstream in the early 1990s. Meanwhile, data volumes have soared into the stratosphere, and the data’s value has risen right along with it.
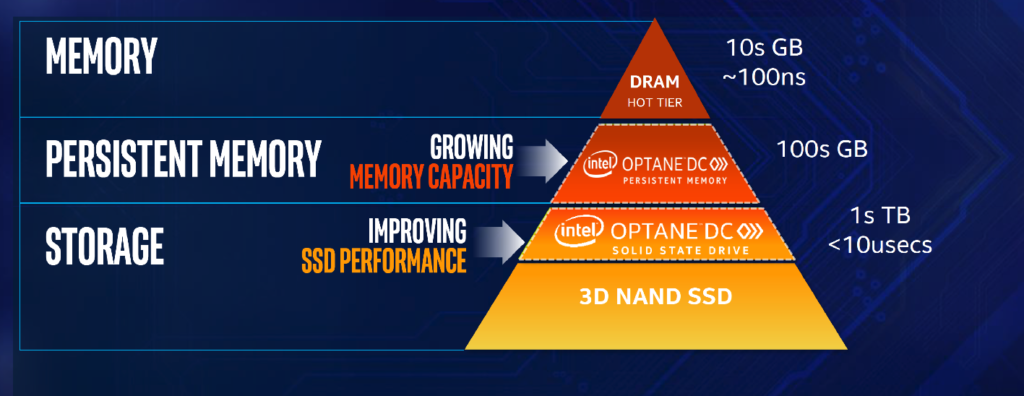
The result: too many memory-bound workloads, with high-performance computing (HPC) end-users caught between the higher cost and limited capacity of DRAM and the lower performance of 3D NAND SSDs.
Intel® Optane™ technology is changing that picture. Available as Intel® Optane™ DC persistent memory and Intel® Optane™ DC Solid State Drives (Intel® Optane™ SSDs), this revolutionary, non-volatile technology closes the capacity, cost, and performance gaps between DRAM and 3D NAND SSDs. In doing so, Intel Optane technology provides exciting opportunities to advance data-intensive workloads while increasing uptime and flexibility in the HPC data center.
Disruptive Memory and Storage Capabilities
Intel Optane DC SSDs are proven technologies that have been helping data centers remove storage bottlenecks and accelerate application performance for the past two years. Now, the launch of Intel Optane persistent memory and the integrated support of 2nd Generation Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors is further shrinking the gap between storage and DRAM. Together, Intel Optane DC persistent memory and Intel Optane SSDs deliver outstanding value across four crucial vectors.
Capacity. Intel Optane DC persistent memory supports more than 3 TB of byte-addressable memory per CPU socket, usable transparently as DRAM or with software optimizations as high-performance storage. In addition, Intel Optane DC SSDs can be used with Intel® Memory Drive Technology software to deliver hybrid memory with traditional Intel Optane SSDs. This makes it possible to switch between storage and extended memory modes on the fly, delivering up to 24 TB of storage-class memory. Users can analyze larger in-memory databases, run higher-resolution simulations, perform more sophisticated graph analytics, and keep up with real-time streaming inputs. Single-node workloads can process larger amounts of data, giving new life to legacy codes and accelerating use cases where datasets must not be split.
Performance. Intel Optane technology delivers dramatic reductions in latency along with consistent read-response times regardless of write loads. Intel Optane DC persistent memory resides on the system bus, bringing data closer to the CPU and reducing latency. Intel Optane SSDs allow for more efficient data caching than NAND-based solutions
Persistence. With Intel Optane DC persistent memory, restart times after a reboot shrink from days or hours down to minutes or seconds. Memory checkpoints can be written and restored quickly, increasing uptime and enabling HPC clusters to operate more efficiently.
Value. Data center managers gain greater flexibility to meet the performance and capacity requirements of diverse workloads—a necessity as HPC infrastructure is increasingly called on to support big data and artificial intelligence workloads as well as modeling and simulation. Storage and memory architects can create larger memory pools, displace DRAM, consolidate storage, or do a mix of all three. High-endurance SSDs and flexible memory/storage options help optimize total cost of ownership.
Start Now, Dream Big
Vast amounts of affordable memory have long been a dream. Now, the dream is becoming a reality. With the disruptive advances of Intel Optane technology, it’s time to reimagine the memory/storage hierarchy for the HPC data center.
Start unleashing a new wave of data-fueled HPC insights today. Explore the resources available on the Intel Optane DC persistent memory and Intel Memory Drive Technology websites, where you will find links to strategic partners offering solutions, and the Developer Zone, with free tools such as the Intel® Persistent Memory Development Kit and Intel® vTune™ Performance Analyzer.
Also check out Intel Optane SSDs to help eliminate data center storage bottlenecks.
__________________
Software and workloads used in performance tests may have been optimized for performance only on Intel microprocessors. Performance tests, such as SYSmark and MobileMark, are measured using specific computer systems, components, software, operations and functions. Any change to any of those factors may cause the results to vary. You should consult other information and performance tests to assist you in fully evaluating your contemplated purchases, including the performance of that product when combined with other products. For more complete information visit www.intel.com/benchmarks.
Intel technologies’ features and benefits depend on system configuration and may require enabled hardware, software or service activation. Performance varies depending on system configuration. No computer system can be absolutely secure. Check with your system manufacturer or retailer or learn more at www.intel.com.
Intel, the Intel logo, Intel Optane, Xeon, and vTune are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and/or other countries.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
© 2019 Intel Corporation