Univa’s Workload Optimization Solution Simplifies Enterprises’ Distributed Datacenters
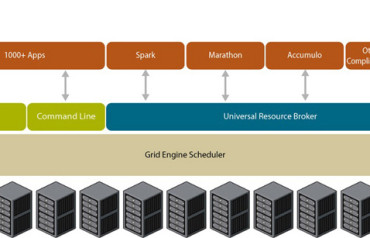
To help enterprises manage and optimize their increasingly distributed applications, datacenters, legacy applications, and frameworks, Univa today took the wraps off Universal Resource Broker, a workload optimization solution for high-performance, containerized, and shared datacenters.
The solution, which is powered by Univa Grid Engine, enables organizations to create one virtual, high throughput, high-performance compute pool out of all their distributed resources, according to the Hoffman Estates, Ill.-based vendor. It integrates distributed application environments that consume dynamic partitions of the cluster and supports a heterogeneous array of machines and environments so businesses can run and manage a combination of bare-metal servers, virtual machines, hybrid clouds and containers, Univa said.
Univa developed Univa Resource Broker in response to existing Univa Grid Engine customers' needs and usage, said Gary Tyreman, president and CEO of Univa, in an interview.
"We were seeing enterprise accounts that were using the technology and they were taking it and using it underneath an internal application they've built. We've seen ISVs join that rank, using the Grid Engine product running apps that used to run on a workstation," he said. "If you can reduce [something] from 100,000 seconds to 500 seconds, who wouldn't want to do that? Now what we're seeing over last 6-9 months, these types of companies – enterprises and existing installed base – new applications factored and rewritten today will use a modern framework with something like Spark or Hadoop. They're building services that are distributed and they're looking for a place to deploy it."
Universal Resource Broker – which can be deployed on Unix, Linux, x86, or RISC servers – provides centralized arbitration and resource allocation; central management for applications, datacenter services, and big data frameworks; policies and lifecycle management, and the ability to run and manage Apache Mesos frameworks without the need to modify them, with high availability and automatic service fail-over.
"ActiveState was an early adopter of the most recent generation of containers and it’s clear from our experience that they will drive much larger computing footprints as their ease and efficiency becomes more accepted," said Bernard Golden, vice president Strategy, ActiveState Software and author of Amazon Web Services for Dummies, in a statement. "This means that managing the much larger underlying infrastructure environments will be a critical challenge. Univa’s Universal Resource Broker will enable organizations to meet that challenge and prepare for a future of container-based application portfolios."
Univa Grid Engine is deployed across more than 10,000 datacenters worldwide, across a diverse mix of industries, said Tyreman. Today, 82 percent of Univa's clients are enterprises, he said. And newer distributed applications in the enterprise now generate about one-fourth of revenue; approximately two or three years ago, they represented only 6% of income, Tyreman said.
Initially, Univa expects Universal Resource Broker to appeal to life science, financial services and data processing – businesses such as media and other data-services organizations, he said. But regardless of vertical market, all prospective and existing clients have similar concerns, Tyreman said.
"Everyone cares about performance and reduction of cost. That's why they rewrite things," he added. "Performance is very key. Our customers tend to call it throughput. They're counting microseconds or milliseconds."
Related
Managing editor of Enterprise Technology. I've been covering tech and business for many years, for publications such as InformationWeek, Baseline Magazine, and Florida Today. A native Brit and longtime Yankees fan, I live with my husband, daughter, and two cats on the Space Coast in Florida.










